
Electronic invoicing aka e-invoicing as a standard and as a process already has a wide acceptance with over 60 countries globally having adopted it. E-invoicing does not mean merely creating an invoice in electronic format but also involves standardization of data to be included, exchange mechanism and involvement of third parties or regulatory authorities to facilitate the exchange.
There are many models followed worldwide for e-invoicing such as
- direct interaction between buyer and seller or
- via a network or clearance model where invoices are routed through tax authorities.
Even in clearance model there are various ways how unique reference number can be generated.
- Either the tax authorities generate the document number and share with the other party, or
- The invoice generation is done by supplier and needs to get stamping from tax authority before sharing with the other party.
1. E-Invoicing in India
India has chosen a variant clearance model and the scope is limited to specified set of businesses and transactions. Here, the responsibility of creating invoices still remains with the businesses, however the created invoice first needs to be registered as per the Government defined practices. Invoices registered with the Government will be considered as valid for any subsequent processes such as sharing with customers, and claiming ITC.
The mandate has been implemented in a phased manner. The ₹500 CR+ turnover companies went LIVE with e-invoicing from October 2020. The next quarter paved the way for ₹100 CR+ turnover companies – mandate went LIVE from 1st January 2021 and now the mandate for small businesses is expected to go LIVE from 1st April 2021.
Updated on 2nd Aug 2022 GST Notification 17/2022 dated 01-08-2022 mandates e-invoicing for taxpayers having AATO above Rs. 10 crores in any financial year since FY 2017-18 w.e.f 1st October, 2022.
E-Invoicing in India goes back to May 2019, when the E-Invoicing Committee was set-up to give their recommendations on the subject. This led to the approval of E-Invoicing implementation in the 35th GST Council Meeting. In October 2019, the proposed framework was released for industry inputs. The e-invoicing portal was released in December 2019 followed by the release of E-Invoicing Schema Version 1.0 and E-Invoice API Specifications Ver 1.0 in January 2020.
The Indian e-invoicing model consists of following components:
- A standard/ Formats for e-invoice – The standard covers the data fields and its specification. It is recommended that businesses (henceforth referred to as taxpayers) should update their systems to follow the e-invoice standard which will allow seamless interoperability and data exchange throughout the eco-system
- A portal for registering invoices – Invoices and other documents such as debit notes, credits notes (henceforth collectively referred as invoices) generated by the taxpayers need to be registered on the Invoice Registration Portal (IRP) and a successful registration will return a unique reference number, digital signature and QR code for the invoice. Only an invoice registered on IRP will be a valid and authenticated document for any further processes such as refund, ITC etc.
1.1 E-Invoice Standard
The e-invoice format prescribed for India has been drafted taking into account the globally followed practices as well as the industry needs of businesses in India. The e-invoice standard has been finalized after consulting with Institute of Chartered Accountants of India (ICAI), the trade bodies and feedback from public.
With the e-invoice standard, the information that taxpayers were including in their invoices in their own silos is now standardized. Taxpayers as per their needs can adopt the fields for reporting, sharing and printing purposes.
One of the important aspects of e-invoicing in India was adoption of a standard for invoice fields. While the GST rules (CGST Rules, Chapter VI, Rule 46) do specify the information to be covered in an invoice, businesses have adopted various practices of reporting the same information on an invoice. Paper or PDF invoicing, the most common form of sharing, are prepared for human consumption. For systems to read and consume, data standardization is the key and that’s what the e-invoice standard aims to achieve. The impact of adopting this standard may not be directly seen by the business users who could be viewing the invoice output the same way as they were earlier, however for systems the data becomes more standardized and hence possibilities of enabling automation in sharing, reading and analyzing opens up. Standardised and structured data fields will make it easier to exchange data electronically and eliminate the need to re-key data and do away with erroneous data input.
The E-Invoice Standard has been put to use through E-Invoice Schema that contains execution related information on various fields to be included in the invoice data.
1.1.1 E-Invoice Schema
The blueprint for e-invoicing in India has been published by the Government specifying the working model of e-invoicing in India along with a standard for generating e-invoicing. The e-invoice schema covers the data fields and its specifications. The GST notification 02/2020-Central Tax, dt. 01-01-2020, lists the data fields and their definitions and GST Notification 60/2020-Central Tax, dt. 30-07-2020 gives updated version(1.1) of the e-invoicing schema
Version 1.0 of E-Invoicing Schema (Released on 2nd Jan 2020):
The First E-invoice schema Version 1.0 shared by the GSTN had about 120 fields, of which about 50 were mandatory to be uploaded on Invoice Registration Portal for obtaining the Invoice Reference Number (IRN) and digital signature. However, later through the year as the GSTN decided to bring the e-way bill generation in line with invoice generation another version of e-invoice schema was introduced covering additional fields for e-way bill generation and other improvements.
Version 1.1 of E-Invoicing Schema (Released on 30th July 2020):
There were not substantial changes in the new E-Invoicing schema. It had major changes to improve the syntax, parameter definitions and specifications. In most of the cases, descriptions (label) and explanatory remarks were reworked.
Following were the changes in the new E-Invoicing schema:
1 New Fields added in the E-Invoicing Schema
2 Changes in Specifications (eg)
As mentioned in point 2 there are some other fields too where maximum length is changed.
3. Changes in Mandatory/Optional Fields (done in lines with EWB schema):
Apart from the above mentioned changes, following points were to be noted:
- Due to the new amount related fields added at invoice level, NIC was expected to change validations related to invoice value.
- B2C added in invoice type is just added in notification as an example however, e-invoicing is not required and will not be allowed for IRN generation.
Currently, there are about 132 data fields listed in the e-invoice standard. out of these 28 are mandatory and 18 conditional mandatory. and for ease of understanding these are broadly grouped as:
- Document details – Document Number, Date and type (Invoice/Credit Note/Debit Note)
- Transaction details – Type of Supply (B2B/SEZ/Export/Deemed Export)
- Buyer and Supplier Details – GSTIN, Legal Name, Address, State, Pincode, Contact details
- Dispatch From – Name, Address State, Pincode
- Ship To Details – GSTIN, Name, Address, State, Pincode
- Item details – HSN, description, quantity, price per unit, taxable value, tax rate and amounts
- Invoice details – taxable value, discount other charges, tax amounts at invoice level, invoice value
- Payment details – Payee Name, Bank account number, mode of payment, credit days, outstanding payment due
- Invoice Reference Details – Contract details, Purchase order details, Project reference No., other reference no.
- Export Details – Shipping Bill No., Date, Port Code, export duty, Additional currency
- Transport details – Distance, Transport Mode, Transporter ID, Vehicle no. and Type in case of Road and Transport Document No. and Date in case of Rail, Ship and Air.
- Other details – Additional document details like URL for supporting documents.
Also to be noted, in case of line item, data will be repeated for every line item.
1.2 E-Invoice Portal (Invoice Registration Portal-IRP)
CBIC vide GST Notification 69/2019 notified the common portal for the purpose of preparation of e-invoice. The portal is termed as Invoice Registration Portal (IRP). Invoices and other documents such as debit notes, credits notes generated by the taxpayers need to be registered on the IRP and a successful registration returns a unique Invoice Reference Number (IRN), digitally signed invoice data and digitally signed QR code for the invoice. Only an invoice registered on IRP will be a valid and authenticated document for any further processes such as refund, ITC etc.
[/vc_column_text]
[/vc_column][/vc_row]Beginner’s guide to
e-invoicing mandate in India
E-invoicing Workflow
Once the invoice is generated by the taxpayers using the accounting and ERP systems, the process of getting the invoice registered with Government on the Invoice Registration Portal (IRP) is to be imitated. Comparing with the current business operations, invoice upload on IRP is new step to be followed.
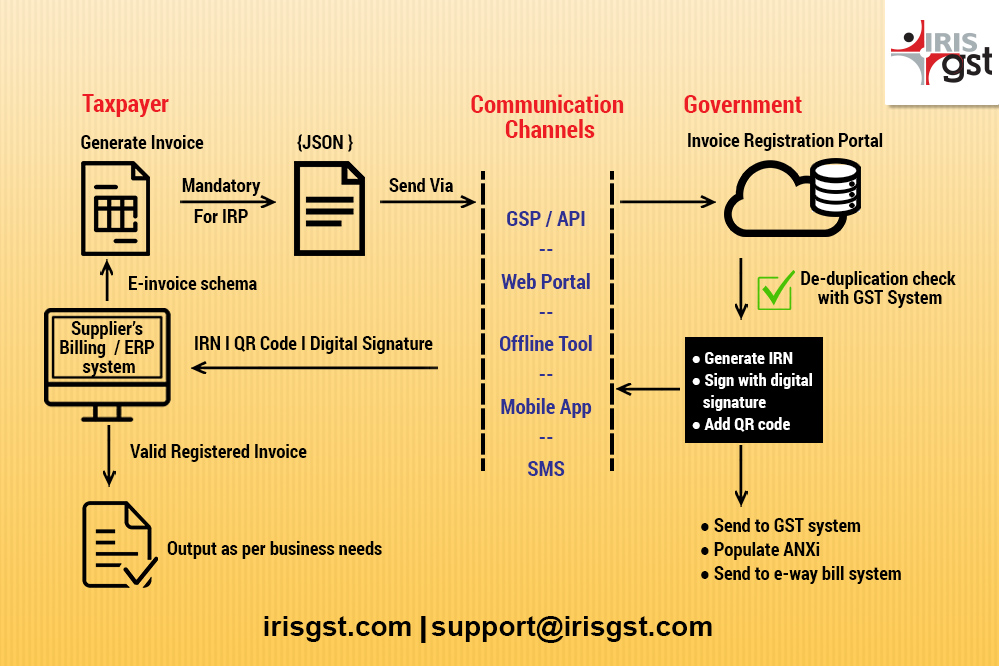
There are two parts of the e-invoicing workflow
- Interaction between Taxpayers and Government
Taxpayers will need to upload the mandatory fields from invoice in JSON format to the IRP. Various modes for upload will be provided such as through GSPs, Offline tool, Web portal, direct API access, mobile app and SMS.
Along with the e-invoice standard, Government has also provided the manner in which unique invoice reference number (IRN) will be created (technically referred as hash using SHA256). Taxpayers have flexibility to generate the IRN also within their systems however the invoice will be valid only when registered with IRP.
The generated or validated IRN, along with QR code and digital signature will be returned to taxpayer via the same communication channels.
- Interaction between IRP, GST and E-way Bill System
Getting invoice registered will be an almost real-time process and hence keeping in view the transaction volume and load on system, the IRP will consist of multiple nodes referred as Registrar. Taxpayers can get their invoices registered through any of the Registrars of IRP system. Further the Registrars will retain data for the last 24 hours.
In order to ensure no duplication, IRP system will be closely connected to the GST system, which will be the central repository for all IRN generated. Given that GST system already has IRN data, populating of ANX 1 for the supplier will be possible.
E-invoice data will also be shared with e-way bill system and the taxpayers or transporters, will simply need to update the Part B information to get a valid Eway Bill Number.
In a nutshell, taxpayers will need to upload invoice data once to IRP and the GST compliance and e-way bill requirements will be taken care of.
E-Invoicing is going LIVE from 1st April 2021: Are You Ready?
Looking at the benefits that theIRP system has to offer, e-invoice standard and the e-invoicing process definitely can be considered as positive changes. Though the scope in the initial phase is limited to B2B transactions, the taxpayers need to take a futuristic and holistic lookout.
Considering the recent updates taxpayers should start the change assessment as the e-invoice standard will imply upgrading the accounting and ERP systems. There will be offline utilities and service providers who can bridge the gap between current systems and expected e-invoice standards, however the full benefits of e-invoicing can only be realized when the IRN and digital signature is recorded back in the accounting systems. In other words, end-to-end integration.
Some key immediate actionable for taxpayers hence are –
- Gap analysis of the e-invoice standard and current captured items in internal invoicing systems
- Change Management: Identify the changes needed, keeping in view, future updates when e-invoice could expand to other transactions such as B2C
- Impact on Other Business Process: Analyze impact on other business processes such as vendor communication, reconciliation, payment milestones etc.
- Supply Chain Evaluation: Evaluate the supply chain gaps and support needs for your small vendors, who will now need to get invoice registered on IRP as only then your ITC claim will be ensured
IRIS E-Invoicing Solution
IRIS is one of the leading GSPs having many large corporate groups using IRIS GST software suite for their GST compliance (IRIS Sapphire), E-way Bill management (IRIS Topaz) and GSTIN verification (IRIS Peridot). IRIS is also one of the free accounting and billing software providers em-paneled by GST for small taxpayers.
We understand compliance and we are also one of the global leaders in implementing standards for regulators and companies.
IRIS Onyx, an e-invoicing solution from IRIS GST, is a one-stop platform for you to view, share and collaborate with your customers and suppliers alike while managing the entire communication with the GST systems in a hassle-free manner.
For any queries or to schedule a demo









































































































































































































































Nice Post
Great post and it is very important for GST user
How can a e Invoice be generated on a State Government Department who is not registered or does not have GSTIN
Treat it as B2C transaction
Hello! I could have sworn I’ve been to this blog before but after browsing through some of the post I realized it’s new to me. Anyways, I’m definitely happy I found it and I’ll be book-marking and checking back frequently!