WFH Positivity Dossier
DAY 2
Hi Folks,
We are back with Day 2 of our #21DayLokdownChallenge! Today we have a very special practise – Shalabhasana that has multiple health benefits. In #EverythingGST we talk about Interest, Late Fees and Penalties and our book of the day is ‘I Will Teach You To Be Rich’ by New York Times bestselling author Ramit Sethi. So wait no more, dive in!
Yoga Pose for the Day
By Meghana Pawar – Certified Yoga Trainer
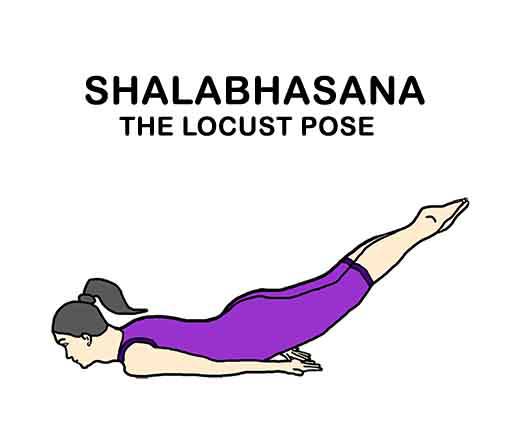
Shalabhasana
Steps to perform the asana:
It is advisable to perform all the asanas on a yoga mat or a sturdy mat that is not slippery.
Step 1: Lie down flat on your stomach in the initial relaxation posture.
Step 2: Bring your right leg in the centre then the left. Now, both your feet, heels, knees and thighs are together. Put your hands close to the body facing the ground.
Step 3: Put your chin on the floor. Raise both your legs up to 30 degree keeping your knees straight.
Step 4: Maintain for 3 to 5 breaths or as per your capacity. And then slowly bring your legs down to relax. Avoid jerks. Repeat for 2 to 4 times as per your capacity.
Note: If you are not comfortable to raise both the legs then start with Ardha Shalabhasana i.e. raising just one leg at a time. And for Purna Shalabhasana you can take support of your fist by putting them in your groin area for comfort.
Avoid if you have Hernia, hyper tension, peptic ulcers, heart problems, or have undergone any recent surgery. Women during pregnancy must avoid.

Regular practice of Shalabhasana can give you the following benefits:
- Strengthens the lower back muscles
- Strengthens pelvic organs, leg muscles, hip joints
- Tones the sciatic nerves. Very good for mild sciatica
- Provide relief in backache, and slipped disc.
- Enhances blood circulation to the spine and the upper body.
- Stimulates the kidneys, liver and all the organs of the lower part of the body.
- Increases abdominal pressure, thus it regulates intestinal function
- Strengthens the abdominal walls.
- Stimulates the appetite.
GST Dossier
Interest, Late Fees and Penalties
Interest and late fees:
Refer below blog for interests and late fees: https://irisgst.com/gst-form-ret-1-how-to-file-table-5-to-table-8/
For Penalties:
Sub-section (1), sub-section (2) and sub-section (3) of Section 122 of CGST Act, 2017, explains certain offences under which penalties are attracted.
Sub-section (1) of Section 122:
Following offences relate to section 122 (1) (i), 122 (1) (ii) and 122 (1) (xix) respectively. Accordingly, such offences occur if as a taxable person;
Make supply of goods or services:
- Without issuing invoice
- Issuing incorrect or false invoice
- Issue invoice or bill of supply without making a supply in violation of the provisions of the Act or Rules.
- Furnish invoice or document using the registration number of another registered person.
I. Offences Involving Fraud
Following offences relate to section 122 (1) (viii), 122 (1) (x) and 122 (1) (xii) respectively. Accordingly, such offences occur if as a taxable person;
- Obtain refund of tax fraudulently
- With an intention to evade payment of tax:
- Falsify or substitute financial records
- Produce fake accounts or documents
- Furnish any false information or return
- Furnish false information with regards to registration particulars either:
- At the time of applying for registration or subsequently
II. Offences Related With Tax Evasion
Following offences relate to section 122 (1) (iii), 122 (1) (iv) and 122 (1) (xv) respectively. Accordingly, such offences occur if as a taxable person;
- Collect tax but fail to deposit it to the government. Provided such a tax is not deposited for a period exceeding 3 months from due date.
- Suppress your turnover leading to evasion of tax.
III. Offences Related With TDS and TCS
Following offences relate to section 122 (1) (v) and 122 (1) (vi) respectively. Accordingly, such offences originate if as a taxable person;
- Fails to deduct tax or deduct appropriate tax as per section 51. Section 51 is applicable for certain specific persons. It requires such persons to deduct tax at the rate of 1 per cent out of the payment to the supplier. Provided the value of supply under the contract exceeds Rs 2.50 Lakhs.
- Fails to deposit the deducted tax to the government
- Fails to collect tax or collect appropriate tax as per section 52. Section 52 is applicable for electronic commerce operators. Such operators are required to collect tax from the supplier at the time of payment. The tax collected should be at the rate of 1 per cent.
- Fails to Deposit the collected tax to the government
IV. Offences Related With Input Tax Credit (ITC)
Following offences relate to section 122 (1) (vii) and 122 (1) (ix) respectively. Accordingly, such offences occur if as a taxable person, you:
- Utilize ITC without actual receipt of supply either fully or partially
- Distribute ITC in contravention of section 20 or rules there under
V. Offences On Account of Failures
Following offences relate to section 122 (1) (xi), 122 (1) (xvi) and 122 (1) (xvii) respectively. Accordingly, such offences occur if as a taxable person;
- Are liable to be registered but fail to obtain registration
- Fail to keep, maintain or retain books of accounts and other documents in the manner prescribed
- Either fails to furnish information or documents called for by an officer. Or furnish false information or documents during any proceedings.
VI. Offences Related With Transportation and Storage
Following offences relate to section 122 (1) (xiv) and 122 (1) (xviii) respectively. Accordingly, such offences occur if as a taxable person;
- Transport any taxable goods without the cover of specified documents
- Supply, transport or store any goods which you believe are liable to confiscation
VII. Miscellaneous Offences
Following offences relate to section 122 (1) (xiii), 122 (1) (xx) and 122 (xxi) respectively. Accordingly, such offences occur if as a taxable person;
- Obstruct or prevent any officer in discharge of his duties
- Tamper with or destroy any material document
- Dispose of or tamper with any goods that have been detained, seized or attached under the Act.
Penalty Levied: in case of any offence mentioned above, you shall be liable to pay a sum which is higher of:
- A penalty of Rs 10,000 or
- An amount equal to the amount of tax evaded
Sub-section (2) of Section 122:
Following offence relates to section 122 (2). These provisions refer to you as a registered person if you supply goods or services on which:
- Any tax has not been paid
- Tax has been short-paid
- Any tax has been erroneously refunded
- ITC has been wrongly availed or utilized
Hence, if you are such a supplier who makes a supply for any of the following two reasons, the penalties attached would be levied.
Reasons for Supply:
Firstly, for reasons other than fraud, wilful misstatement or suppression of facts to evade tax. In such a case, you as an offender shall be liable to pay a penalty which is higher of:
- A sum equal to Rs 10,000 or
- 10 per cent of the tax due from such a person
Secondly, for any reason of fraud or wilful misstatement or suppression of facts to evade tax. In such a case, you as an offender shall be liable to pay a penalty which is higher of:
- A sum equal to Rs 10,000 or
- 100% of the tax due from such a person
Sub-section (3) of Section 122:
Following offences relate to section 122 (3). These offences deal with the situations where you are not directly involved in tax evasion. Instead, you aid or abet or may be a party to such an evasion. Furthermore, it also includes cases where you do not attend summons or produce documents.
I. Accordingly, those cases are as follows:
- Aiding or abetting any of the offences specified in clauses (i) to (xxi) of sub-section (1)
- Acquiring or concerning with goods which are liable to confiscation. It includes transporting, removing, depositing, keeping, concealing, supplying, purchasing or other ways of dealing with goods.
- Failing to issue an invoice in accordance with the provisions of the Act or Rules. Or failing to account for an invoice in books of accounts.
- Receiving or concerning with the supply of services which are in contravention of the provision of the Act or Rules. It also includes any other manner of dealing with such a supply of services.
- Failing to appear before the officer of the Central Tax. Provided you are issued with summon for appearance in an inquiry. And you are supposed to give evidence or produce any document in such an inquiry.
Penalty: If you as an offender commit any of the above offences, then you shall be liable to pay a penalty which may extend to Rs 25,000.
II. Penalty for Failure to Furnish Information Return (IR)
Under the CGST Act, 2017, section 123 deals with circumstances where you fail to file an Information Return under section 150.
Section 150 lays down cases where you are obligated to furnish an Information Return. If you fail to furnish an Information Return in such cases within a stipulated period, it calls for a penalty. The stipulated period to file Information Return is 30 days from the date of issue of show cause notice.
Penalty: If you fail to file IR within stipulated time, you shall be liable to a penalty of Rs 100 each day for which the failure continues. Such a penalty cannot exceed Rs 5,000.
III. Penalty for Failure to Furnish Statistics
Section 124 of the CGST Act, 2017, deals with penalty levied in circumstances where you fail to furnish information under section 151.
According to section 151, a Commissioner has the power to collect statistics concerning any matter dealt with under the Act. He may issue a notice asking you to furnish information or returns in a prescribed format. Such information relates to the matters for which statistics are to be collected.
Therefore, section 124 specifies penalty for failure to provide information or return in two circumstances:
- Failing to furnish such information or return without reasonable cause
- Wilfully furnishing or causing to furnish any information or return which is known to be false
Penalty: If you fail to furnish such information, you shall be liable to a fine of up to Rs. 10,000. But where the offence is continuing, a further fine of Rs 100 is levied each day for which the failure continues. However, such a penalty cannot exceed Rs 25,000.
IV. General Penalty
Section 125 of the CGST Act, 2017, deals with such cases where no separate penalty is prescribed under the Act or Rules. Accordingly, it refers to cases where you contravene
- Any of the provisions of the Act or
- Rules made there under
Provided, there is no penalty separately prescribed for such an offence under the Act.
Penalty: The penalty imposable in such a case is up to Rs 25,000.
V. Punishment for Certain Offences
Section 132 of the CGST Act, 2017 describes cases of tax evasion and the penal actions applicable on specific events. This section provides for cases where your offences lead to prosecution and accordingly a punishment is initiated on you. The term prosecution means conducting legal proceedings against an offender before a legal tribunal. And the punishment for such an offence involves either imprisonment or fine or both.
A. This part enumerates cases identified by law makers as offences liable for prosecution:
- Supplying goods or services or both without the cover of invoice. Provided it is done with the intention of evading tax.
- Issuing any invoice or bill without actual supply of goods or services or both. Provided such an act leads to wrongful input tax credit or refund of tax.
- Availing ITC using invoice referred to in point (ii) above.
- Collecting taxes without any payment to the government for a period exceeding 3 months from due date.
- Evading tax, availing credit or obtaining refund with the intent of fraud. Where such offence is not covered in clause (i) to (iv) mentioned above.
- Falsifying financial records or producing false records/ accounts/ documents/ information. Provided it is done with the intention of evading tax.
- Obstructing or preventing any officer from doing his duties under the act.
- Acquiring or transporting or in any manner dealing with goods liable for confiscation under this Act.
- Receiving or dealing with supply of services which are in contravention of any provisions of this law.
- j. Tampering or destroying any material evidence or documents.
- k. Failing to supply information which a person is required to supply under this law or supplying false information.
I. Attempting or abetting the commission of any of the offences mentioned above.
Now, this section enables commencement of prosecution proceedings against the offenders. It also lists the period of imprisonment and quantum of fine for all such prosecution offences. Such a punishment varies depending on the amount of tax evaded or seriousness of the offence as listed below.
B. This part deals with persons committing any offence specified in clause (vi), (vii) or (x) above. Such offenders shall be punishable with:
- Imprisonment for a term which may extend to six months or
- Iine or
- Both
C. This part deals with repetitive offences.
There are cases where you are convicted of repetitive offences. And such offences without any specific/special reason are to be recorded in the judgment of the Court. Such offences will entail an imprisonment term of not less than 6 months. But such imprisonment could extend to 5 years plus a fine.
D. All offences mentioned in this section are non-cognizable and bail able except the following cases:
(i) Where the amount exceeds 5 Crores and
(ii) Instances covered by (a) to (d) in Para A.
Book of the Day
Title: I Will Teach You To Be Rich
Author: Ramit Sethi

- Living a rich life: Ramit Sethi, the NewYork Times Best Selling Author is also a very successful entrepreneur. He guides his followers about personal finance and often talks about the importance of defining what a ‘rich life’ means to us. Every person’s definition of a rich life will be different. Not everyone’s rich life will include billions of dollars, for some it may be physical fitness, happiness of their loved ones or simply financial freedom. He tells his readers to define their live a rich life and have a plan to live it.
- Picking the right bank accounts: The book has a six week program that can help you become rich. One of which is choosing the right back accounts that offers maximum interests and requires us to have minimum balance facility. He also suggests having multiple savings accounts. Be aware of the money that you are making and regularly check with it.
- Conscious Spending: Ramit always emphasises conscious spending. Conscious spending does not mean not buying what you love and living like a miser. In fact, he suggests spending on what you love with an open heart and cut back on what you don’t.
- Automate your investing: Investing is another very important aspect that is being discussed in the book in detail. Not just automate investing but automate whatever is possible and not let small decision making to consume one’s energy.
- Focus on Getting Things 85% Right: The author says, one should not keep worrying about perfection. One must focus on getting things done even if they are 85% right. Important is to get this moving and finish what you start.
This was Day 2 of our #WFHPositivityDossier. Coming up we have lots more interesting stuff so stay tuned!!








































































































Leave a comment