In this article, we will discuss in detail about Input Service Distributor (ISD) under GST, its definition, eligibility criteria, and its functioning. We will also explore what is form GSTR-6, its filing process, and due dates of the return. So, if you are a business owner or a taxpayer who wants to understand the concept of ISD and GSTR-6 filing under GST, this article is for you.
New Update
Notification No. 16/2024-Central Tax, dated 6th August 2024
Prior to this notification, the ISD mechanism was not mandatory. However, through this amendment to Sections 2(61) and 20 of the CGST Act, 2017, the government has mandated the ISD provisions, effective from 1st April 2025.
Union Budget 2025
The Union Budget 2025 introduced amendments to Sections 2 and 20 of the CGST Act, explicitly incorporating the reverse charge mechanism provisions outlined under Sections 5(3) and 5(4) of the IGST Act.
Role of an Input Service Distributor
Input Service Distributor means an office of the supplier of goods or services or both which receives tax invoices issued under section 31 towards the receipt of input services and issues a prescribed document for the purposes of distributing the credit of central tax, State tax, integrated tax or Union territory tax paid on the said services to a supplier of taxable goods or services or both having the same Permanent Account Number as that of the said office.
The concept of Input Service Distributor (henceforth referred to as ISD) was introduced for those businesses which have common expenditure across its business locations across the country, but the invoicing/billing is done usually to a centralized location. As the name suggests ISD registration can be used for credit distribution on the supply of services only and not goods.
There are two important roles of an Input Service Distributor:
- ISD receives the invoices for the common services from service providers who charge GST from the ISD.
- ISD issues invoices to the respective units who actually receive the services but having same PAN as that of the ISD registration and thereby distribute the tax paid to such service providers. As the services are not actually consumed by the ISD, he cannot claim input tax credit for the tax paid and hence he has to distribute the same to actual service recipients within same PAN (henceforth referred to as service recipients).
Regular Taxpayer vs. Input Service Distributor
Few major differences between a normal taxpayer and an ISD taxpayer are:
- An ISD taxpayer does not have any outward supplies like a normal taxpayer.
- An ISD and normal taxpayer both have inward supply invoices but an ISD cannot claim credit for the tax paid on services provided like a normal taxpayer.
- A normal taxpayer files GSTR 3B through which liability and input tax credits are posted to the respective ledgers maintained by GSTN. However, ISD does not have to file GSTR 3B as it neither has any liability of its own nor credits and therefore no ledgers as well.
Let’s understand this with an example:
Entity A has two registrations in Maharashtra; one as Normal Taxpayer and another as an Input Service Distributor. So normal supplies of goods/services by A from Maharashtra will have to be reported by A in GSTR 1 of the normal taxpayer GSTIN and not in ISD registration. Suppose B is a vendor who provides services to A at all three locations. Now B has two options for billing A. He can prepare three separate bills for all three locations on their normal GSTINs or another option for him is to bill A on his ISD registration. ISD registration of A will then distribute the tax credit between the other three GSTINs by issuing separate documents.
How to identify the registration type of a Taxpayer? Check the GSTIN in IRIS Peridot, a handy and easy-to-use mobile application, which provides details of a GSTIN when scanned. You can know the type of registration and ensure that you are billing to the right party.
Rules for ITC distribution for Input Service Distributor
Some important points to be noted while distributing input tax credit for Input Service Distributor are as follows:
- Credit available can be distributed only against an ISD Invoice containing the prescribed details as mentioned in Rule 54 of CGST rules, clearly indicating in such invoice that it is issued only for distribution of input tax credit.
- Credit can be reduced only through issuing an ISD credit note containing the prescribed details as mentioned in Rule 54 of CGST rules.
- Amount of input credit distributed should not exceed the amount of credit available for distribution.
- Credit of tax paid on input service attributable to a recipient shall be distributed only to that recipient.
- Credit of tax paid on input service attributable to more than one recipient shall be distributed pro-rata on the basis of the turnover of such recipient to the aggregate of turnover of all such recipients to whom such input service is attributable and which are operational during the year.
- Credit of tax paid on input service attributable to all recipients shall be distributed pro-rata on the basis of the turnover of such recipient to the aggregate of turnover of all recipients and which are operational during the year.
- Input tax credit available for distribution in a month shall be distributed in the same month.
- Input Service Distributor shall separately distribute the amount of ineligible input tax credit and the amount of eligible input tax credit.
- Input tax credit on account of IGST/CGST/SGST to be distributed separately.
- Input tax credit that is required to be distributed to one of the recipients ‘R1’, whether registered or not, from amongst the total of all the recipients to whom input tax credit is attributable, including the recipient(s) who are engaged in making exempt supply, or are otherwise not registered for any reason, shall be the amount, “C1”, to be calculated by applying the following formula –
- C1 = (t1÷T) × C
where,
“C” is the amount of credit to be distributed,
“t1” is the turnover, as referred to in section 20, of person R1 during the relevant period, and
“T” is the aggregate of the turnover, during the relevant period, of all recipients to whom the input service is attributable in accordance with the provisions of section 20;
- C1 = (t1÷T) × C
- Input tax credit on account of IGST shall be distributed as IGST.
- Input tax credit on account of CGST and SGST/UTGST shall be distributed in following manner :
- If the recipient is located in same state or union territory in which ISD is located, CGST shall be distributed as CGST and SGST/UTGST shall be distributed as SGST/UTGST.
- If the recipient is located in different state or union territory other than that of ISD, CGST shall be distributed as IGST and SGST/UTGST shall be distributed as IGST.
- Input tax credit required to be reduced on account of issuance of a credit note to ISD by the supplier shall be apportioned to each recipient in the same ratio in which the input tax credit contained in the original invoice was distributed in terms of clause (d), and the amount so apportioned shall be-
- reduced from the amount to be distributed in the month in which the credit note is included in the return in FORM GSTR-6; or
- added to the output tax liability of the recipient where the amount so apportioned is in the negative by virtue of the amount of credit under distribution being less than the amount to be adjusted.
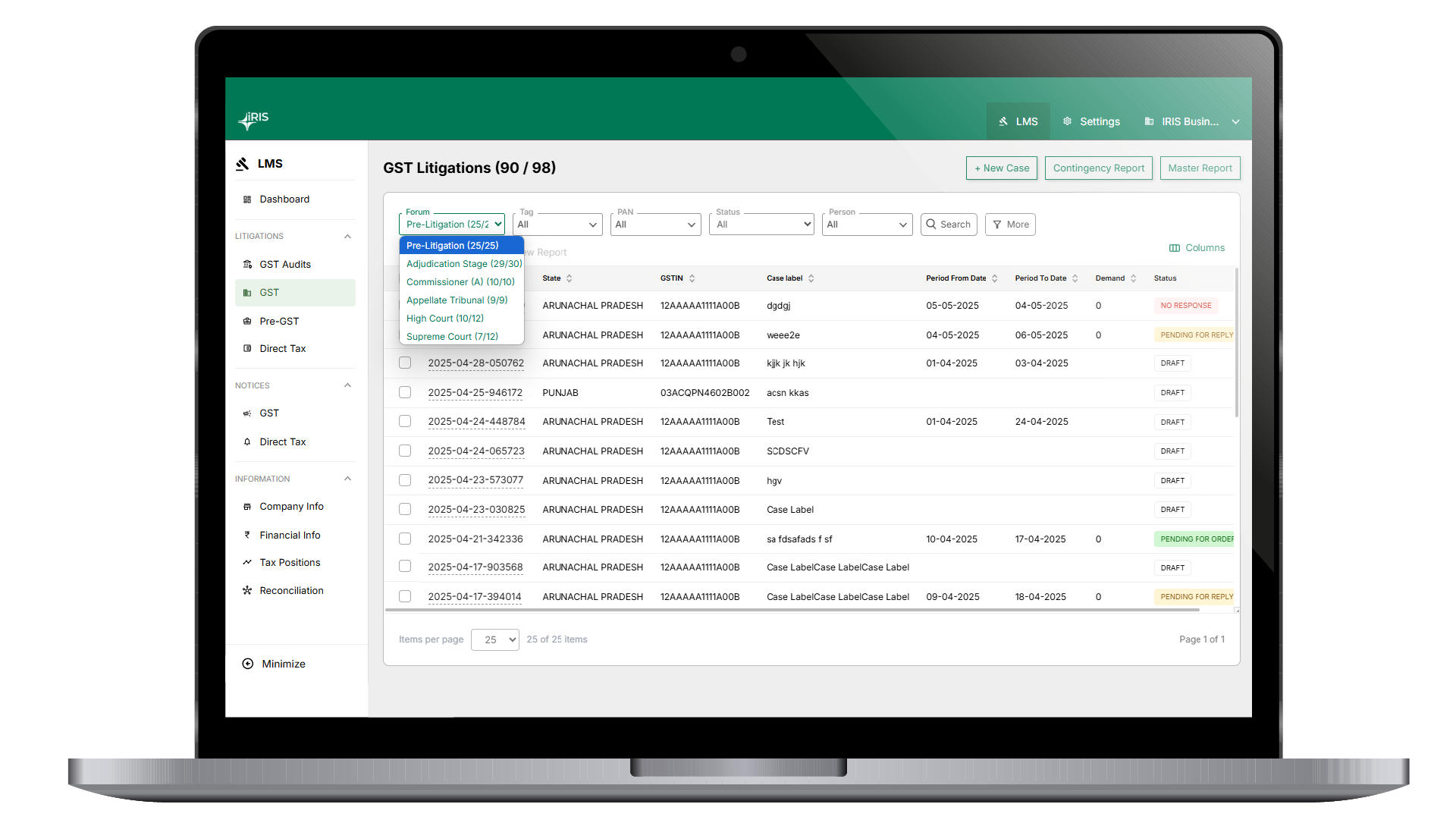
Which form ISD needs to file? What is GSTR 6
GSTR 6 is a GST return form that has to be filed monthly by the businesses that have taken registrations as Input service Distributors.
Due Date for Filing GSTR 6
Return filing due date for GSTR 6 for a particular month as per CGST Act is 13th of the next month.
GSTR-6 is divided majorly into two sections:
1. B2B and CDN Section (Actionable Auto-drafted details)
- Accept: Accept action implies that the invoice is being accepted and the amount of tax paid in the invoice is available for distribution.
- Reject: Reject action implies that the invoices are being rejected and the amount of tax in that invoice is not available for distribution. Reject action is usually to be taken when the invoice either does not belong to ISD. The invoices that are rejected by ISD in this section get auto-populated in GSTR-1 of the vendor.
- Pending: The invoices that are kept pending in this month imply that invoices are not yet received the ISD and hence ISD cannot distribute ITC for these invoices in the current month. These invoices get will get carried forward in the GSTR 6A of next month of ISD after the current month is filed.
- Adding new invoices: Some vendors may have either missed some invoices to be submitted in their GSTR1 or may not have filed their GSTR1. Hence these invoices can be uploaded by the ISD as missing invoices. These invoices also get populated in GSTR-1 of the vendor.
2. ISD Section(ITC distribution details)
In this section, the ISDs are required to upload the invoices and credit notes issued by them to the service recipients for input tax credit distribution. These invoices and credit notes will form part of GSTR 2A/ 2B of the service recipients. The manner of distribution of credit by ISD is laid down under section 20 of CGST Act and additionally Rule 39 of CGST Rules provides for the procedure and calculation for distribution subject to certain conditions explained above.
Apart from these in case of any amendments are present in the B2B and CDN section due to which the amount distributed as credit is reduced then the procedure for reducing the credit will be the same as followed for a reduction in case of a credit note.
Filing GSTR 6
The filing of GSTR-6 is much simpler from a compliance point of view as partially the return is auto-populated. However, in order to take corrective actions on the auto-populated invoices, it is equally important to reconcile the data with the purchase register of ISD. As there are various common services involved in each business, it is obvious that a lot of invoices do get auto-populated in GSTR 6.
An auto-reconciliation process that can automatically classify invoices into match and mismatch categories and even provide details of missing invoices either in GSTR 6A or your purchase register, will make your return filing process efficient.
Check out our GSTR 6 return filing and process and auto reconciliation feature which works for GSTR2 as well as GSTR6. To know more about how this auto-reconciliation works through our GST Filing Software, or for any other queries on GST return filing process, please write to support@irisgst.com.